¿Buscas implementar un ERP, pero no conoces que compone su costo? ¿Cómo sabes cuál es la mejor opción? ¿A largo plazo, cuánto dinero estarás invirtiendo? ¿Cuáles son los costos ocultos?. Este blog post ofrece una guía clara de los componentes que conforman el costo de un ERP y las diferentes opciones por si aún sigues dudando sobre implementar uno en tu empresa.
Este blog post es un recuento de una entrevista interna con nuestra Directora de ventas Viviana Muñoz donde conversamos sobre aquellos componentes que conforman el costo de un ERP. Su experiencia en el mundo de los ERP: Consultora ERP, con experiencia en implementación de proyectos de manufactura, construcción, proyectos, renta y distribución. Gerente comercial de partner de SAP en LATAM y Socia - Directora Comercial de Vauxoo partner # 1 de Odoo.
Index
Licensing
Perpetual licensing
What are the benefits of this model?
What disadvantages does this model have?
What are the benefits of this model?
What disadvantages does this model have?
If we make a cash flow projected to five years, what could be the results depending on the types of ERP in licensing matters?
Odoo
Dynamics
SAP
Implementation service
Odoo
SAP
Infrastructure
Purchase of the infrastructure
Hosting
SaaS Model
Support
Of the different ERP solutions, is there a hidden cost in any of its components?
In software licenses
In deployments
In infrastructure
What happens in the long term with the budgets projected at the beginning of the project?
Not being clear about how much the next phases will cost and if the selected ERP has the necessary tools to implement it
Not acquiring an ERP that have a solution for different industry verticals
Selection of a software that does not allow decreasing
How can I calculate the cost of an ERP solution?
Para toda empresa que busque implementar un Sistema de Planificación de Recursos Empresariales (ERP) el precio es uno de los factores más importantes. Sin embargo, poco se habla de cuál es el costo y que la compone. Para calcular el costo de una solución ERP se toman en cuenta cuatro componentes:
Licenciamiento perpetuo o suscripción
El servicio de implementación
Infraestructura
Soporte
Licenciamiento
El primer componente responde a las preguntas ¿Qué tipos de licenciamientos existen? ¿Qué ventajas y desventajas representan?
Los ERP ofrecen diferentes tipos de licenciamiento dependiendo del modelo, existen dos modelos: Licenciamiento perpetuo y suscripción.
Licenciamiento perpetuo
Las licencias perpetuas son un derecho de uso que adquiere el comprador para utilizar el software de manera perpetua. Al adquirir este tipo de licenciamiento, implícitamente el comprador acepta un contrato de pago anual del mantenimiento del producto, con porcentajes que oscilan entre el 15 y el 22% anual del valor pagado por el licenciamiento, este porcentaje varía dependiendo del ERP.
Este es un modelo que aún se conserva en soluciones cómo SAP.
What are the benefits of this model?
En algunos países de Latinoamérica, por tratarse de un activo fijo, es posible recibir financiamiento para su compra y por ser un activo fijo, podrá ser depreciado y representa un mayor valor del costo.
What disadvantages does this model have?
No es posible reducir los usuarios adquiridos, si tu compañía compró 100 usuarios y a futuro redujo sus empleados a 50 usuarios, deberá seguir pagando el contrato de mantenimiento por los 100 usuarios a perpetuidad. Compañías que manejan Puntos de Ventas, agencias, y contratación por proyectos son las más afectadas por este modelo rígido (no escalable en usuarios).
Representa una alta inversión inicial en licenciamiento y puede representar un gran impacto en el flujo de caja.
Aun cuando es un activo fijo, por tratarse de un derecho de uso, en caso de liquidación de la compañía, no podrá ser comercializado.
Software as a service (SaaS)
En este modelo el ERP el software es accesible para los clientes a través de internet mediante el pago por uso. El proveedor del ERP administra el hardware, el middleware, el software de aplicaciones y la seguridad. El licenciamiento del modelo SaaS funciona con base en una suscripción que puede ser mensual o anual. En este modelo podemos encontrar soluciones como Oracle, Dynamics, y Odoo.
What are the benefits of this model?
Normalmente estos servicios se encuentran en alojamientos en la nube compartidos por lo cual representa un bajo costo de mantenimiento.
Cuentan con soluciones para desplegar, escalar y actualizar el ERP con mayor rapidez.
Permiten proyectar el costo del ERP con mayor precisión.
No requiere una inversión tan alta, como la realizada en el licenciamiento a perpetuidad.
What disadvantages does this model have?
Considero que con la nueva realidad, ya no existen desventajas sobre este modelo.
If we make a cash flow projected to five years, what could be the results depending on the types of ERP in licensing matters?
Mostrando una comparación del costo de licenciamiento por usuario en el modelo SaaS de las soluciones para medianas empresas de algunos ERP:
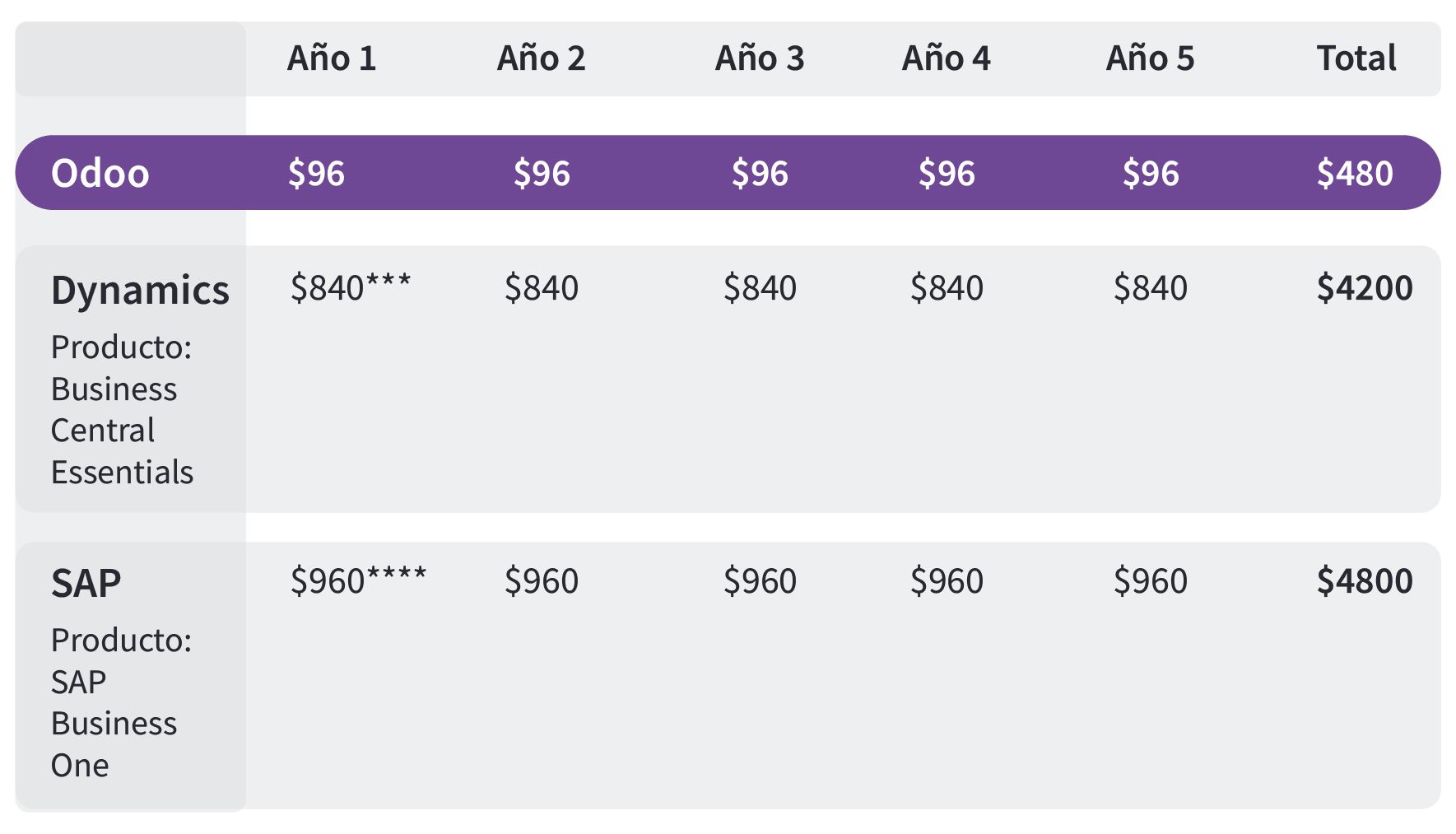
Sin embargo, el valor de licenciamiento por usuario nombrado, no es el único componente del costo de licenciamiento. Existe un segundo factor que corresponde a los módulos que requieren acceso los usuarios.
Odoo
En Odoo no se paga valor adicional usuario por módulo, sino que se paga un monto fijo anual por el módulo y puede ser habilitado en los usuarios adquiridos, los valores de los módulos son desde 4 usd/mes. Al adquirir la suscripción a un módulo cualquier usuario contratado podrá utilizar los módulos sin ninguna restricción, ni costo adicional.
Dynamics
El valor incluido (***equivalente a 70 Usd no incluye los módulos de producción y servicios) en caso de requerir incluirlos el valor asciende a usd 100. Si adicionalmente el usuario requiere acceso a CRM o módulo de ventas, se requieren dos licencias diferentes.
SAP
En SAP se manejan dos tipos de licenciamiento en la modalidad de licenciamiento perpetuo, 1) licencia profesional y licencia limitada (puede elegir entre limitado a finanzas, limitado a logística o limitado a ventas). En caso de que se requiera habilitar permisos a usuarios para módulos fuera del alcance de la licencia, se deberá realizar un Upgrade a licencia profesional, lo cual casi que duplicaría el valor. Tener en cuenta que adicionalmente se requiere el pago del mantenimiento de las licencias equivalente al 17% de la suma de los licenciamientos.
Servicio de implementación
El segundo componente corresponde al servicio de implementación, este componente responde a la pregunta: ¿Qué tipos de implementación existen?
Este punto está directamente relacionado con la metodología de implementación sugerida por cada fabricante de ERP y por el implementador (Partner).
Actualmente la mayoría de ERPs de talla mundial, manejan un modelo de implementación a través de partners certificados. Estos sucede en el caso de Oracle, Dynamics, SAP y Odoo.
Odoo
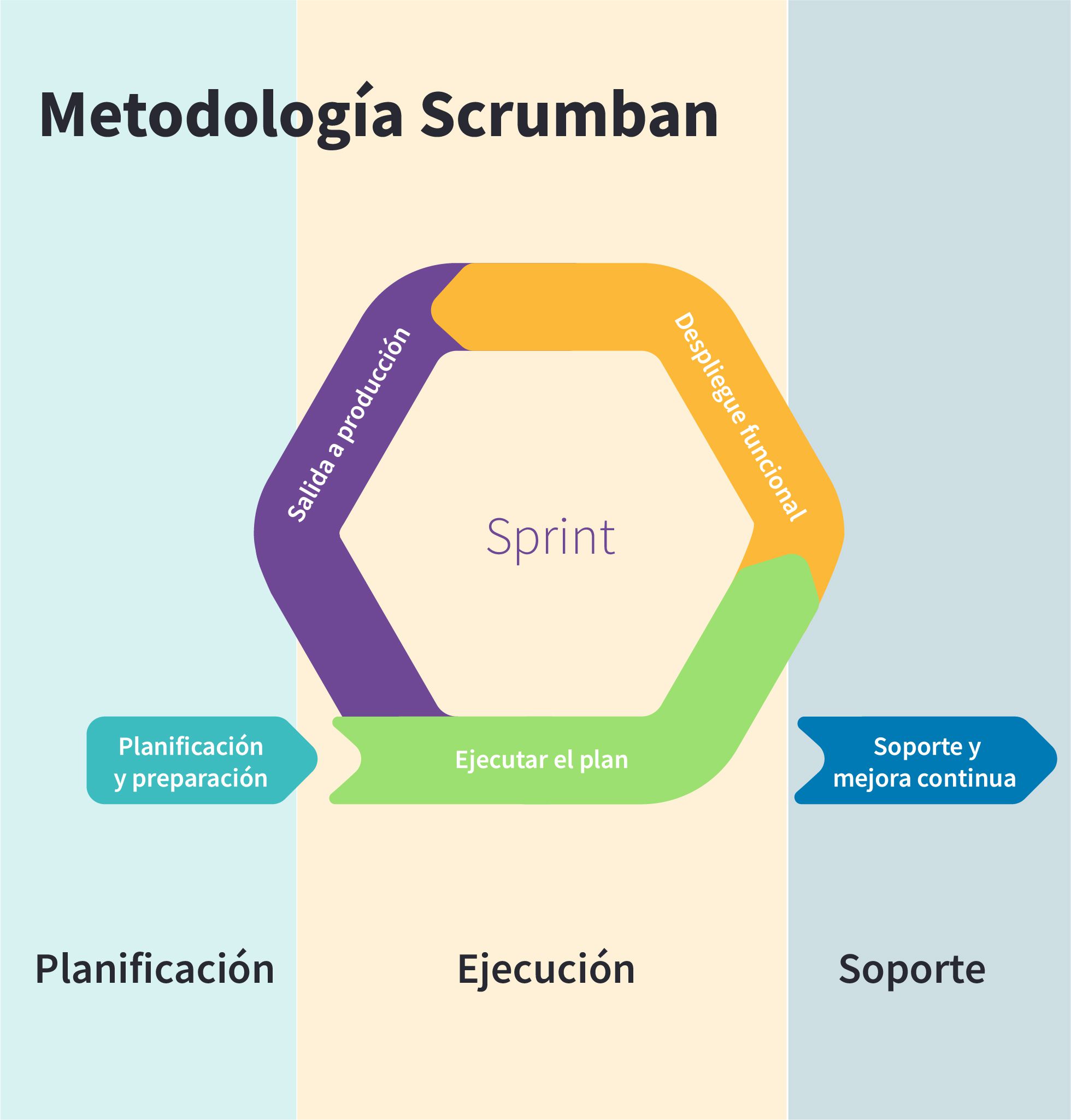
Odoo es una herramienta que utiliza metodologías ágiles para la implementación. Vauxoo, como partner número 1 de Odoo, utiliza Scrumban como metodología de desarrollo.
Se trata de una metodología ágil basada en Scrum, que adopta varios conceptos de Kanban y de LEAN para aliviar el framework y dedicar más tiempo a actividades de alto valor.
Scrumban no tiene ciclos de trabajo rígidos, sino que son flexibles, disparando los “sprint meetings” y el inicio del siguiente ciclo basado en ciertas condiciones.
El proyecto inicia con una fase de planificación única que durará aproximadamente 1 mes, de seguido se realizarán una a una las iteraciones o fases que constan de 3 etapas cada una según se muestra en el siguiente gráfico.
SAP
Mientras que por otro lado SAP utiliza una metodología ASAP (Accelerated SAP) para la implementación:
Preparación del proyecto: definición de objetivos, selección de los recursos humanos, definición de roles y responsabilidades, etc.
Blueprint: se realiza un proceso de documentación, se elabora el diseño de la solución a nivel técnico y funcional.
Realización: se elaboran los ajustes básicos para realizar personalizaciones del software a los procesos de negocio, se procede a su validación, migración de datos, informes.
Preparación final: en esta fase se llevan a cabo pruebas unitarias e integrales y se testea la integración del software con los procesos. Se capacita a usuarios finales.
Soporte go-live: se proporciona el apoyo necesario al personal durante la fase de arranque del sistema, especialmente en los primeros días, aunque la fase de soporte se puede dilatar en el tiempo porque se requiere estabilizar al tiempo todos los módulos.
Por lo general, ambos modelos de implementación cuentan con tarifas recurrentes para la capacitación, el soporte y el mantenimiento continuo. Las tarifas dependen de los países. En LATAM son comunes tarifas entre 50 usd y 90 usd la hora, y un proyecto estándar de distribución, o venta de servicios de menos de 50 usuarios podría implementarse entre 400 a 700 horas dependiendo de la metodología utilizada.
La diferencia radica en que las metodologías ágiles de implementación utilizadas en el ERP Odoo, permitirán obtener victorias rápidas y por tanto un rápido retorno de la inversión, adicionalmente tienen el beneficio de que las inversiones suelen ser por fases.
En metodologías más rígidas, que no permiten implementación modular, normalmente es requerida una alta inversión desde el inicio y los resultados se podrán ver hasta que todo el ERP esté implementado.
La infraestructura
El tercer componente es la infraestructura, este responde a la pregunta: ¿Qué modelo de infraestructura voy a utilizar?
Compra de la infraestructura
En este modelo el cliente compra los servidores y lo aloja en un servicio de datacenter (housing) o en sus instalaciones.
Hosting
En este modelo se utiliza un proveedor de servicios como OVH, Google, Azure, o alguna compañía que ofrece servidores en la nube para instalar y mantener el software. Normalmente requiere herramientas de despliegue.
Modelo SaaS
En el caso de las soluciones SaaS el software se aloja en los servidores internos del proveedor del ERP, por lo tanto el cliente no se encarga del mantenimiento de la infraestructura.
Soporte
Una vez está en producción el ERP, y se ha estabilizado, normalmente se requieren servicios de soporte del implementador.
Existen básicamente tres modalidades de pago de soporte dependiendo el ERP y el implementador, 1) Contrato de soporte recurrente con un valor y alcance fijo, 2) paquetes de soporte por horas o tickets y 3) Soporte postpago.
Of the different ERP solutions, is there a hidden cost in any of its components?
Si, muchas veces existen costos que no están implícitos en el servicio contratado. Para mantener la estructura de la respuesta anterior, clasificaremos los costos ocultos que se podrían presentar en:
Licenciamiento
El servicio de implementación
Infraestructura

En licencias de software
El costo de que un usuario acceda a un módulo adicional (no incluido en la contratación) representa el costo oculto más típico y en muchos casos, no es un caso menor. Recomiendo en la preventa, consultar con su asesor el impacto de que un usuario pueda requerir acceso a módulos adicionales.
En implementaciones
Dos de los costos ocultos más recurrentes son:
El desconocimiento de los términos y condiciones de los llamados “proyectos llave en mano”, en los que se vende un alcance de proyecto, y el cliente no lleva control de las horas invertidas. Es claro que la empresa consultora, debe proteger el alcance del proyecto para obtener una rentabilidad, por lo que es necesario leer a detalle la letra pequeña de los términos bajo los cuales es un proyecto cerrado, ejemplo. Hasta 5 aprobaciones, hasta 3 informes, hasta 10 campos personalizados, no incluye desarrollos, etc. Es necesario solicitar a su preventa, le notifiqué los alcances y limitaciones para que queden documentados.
En proyectos que son cotizados por hora de consultoría, el no contar con un partner experto podría subestimar las horas de implementación y no estimar correctamente desarrollos o personalizaciones. Esto podría hacer que el cliente presupueste un alcance y finalmente por la inexperiencia del consultor termine pagando un valor diferente.
En infraestructura
Cuando no se trata de un hosting, sino instalación en los equipos del cliente, varios ERP utilizan Windows server para poder ser instalados y requieren este tipo de licenciamiento o licenciamientos de herramientas como terminal server para un acceso remoto.
Eso es un costo oculto, ya que muchas veces las compañías no lo ven hasta que se comienza la implementación y no están dentro de la cotización del ERP porque eso no es parte del producto.

What happens in the long term with the budgets projected at the beginning of the project?
Hay tres factores que en mi experiencia he visto que desbordan los presupuestos a futuro.
Not being clear about how much the next phases will cost and if the selected ERP has the necessary tools to implement it
Es claro que en una primera fase, las compañías buscan resolver la operación interna, el core business o como se le conoce “organizar la casa”, sin embargo, en esta nueva realidad las empresas necesitan soluciones flexibles, versátiles y orientadas al futuro que les permitan cubrir la operación de la compañía y además proporcionar herramientas integradas al ERP y que ayuden tanto a automatizar la operación como a mejorar la experiencia del cliente.
Cuando un ERP no cuenta con estas herramientas, las empresas tendrán problemas en el futuro, ya que no podrán encarar de mejor manera los desafíos actuales (Esquemas de trabajo remoto, la digitalización empresarial, Marketing 5.0, entre otros). En este momento, lastimosamente las empresas se verán forzadas a incurrir en desarrollos o a contratar integraciones con otros software para cubrir estas necesidades, generando un desbordamiento de los costos y tiempos del proyecto.
Not acquiring an ERP that have a solution for different industry verticals
Las compañías están en constante cambio, por lo que requieren soluciones que ofrezcan diferentes verticales de industria, para garantizar la escalabilidad al sistema a nuevos modelos de negocio.
Selección de un software que no permite decrecer
El seleccionar un software que no les permita decrecer en módulos o licencias es una afectación directa al flujo de caja de la compañía. Normalmente las empresas tienen como objetivo crecer y aumentar su cartera de clientes, pero a veces por diferentes factores los clientes pueden disminuir y las compañías deben seguir pagando anualidades por haber adquirido modelos de licenciamientos perpetuos con anualidades de mantenimiento y cláusulas que no les permiten decrecer en número de licencias de uso.
La búsqueda de un ERP que genere valor toma de tiempo, conocer los componentes que conforman su costo genera una idea más clara para la elección del ERP que más se adecue a las necesidades de tu empresa. Se debe asegurar un enfoque claro de las características que serán requeridas a un corto, mediano y largo plazo para la correcta elección de un ERP.
* Odoo. Valor por usuario nombrado año para proyectos SaaS, para implementaciones estándar. Incluye hosting del fabricante. No incluye el valor de los módulos debido a que no se cobra por usuario.
**Dynamics. valor usuario nombrado al año 70 usd al mes para implementación estándar (no incluye módulos de Manufactura, ni servicios), incluye hosting.
*** Value per named user per year with limited license (logistics, financial or sales). The value varies for professional licenses. SAP as a manufacturer does not offer direct hosting, it is required to contract a hosting service with a third party, or multi tenancy servers with the Partner. Included in the value presented