The use of an ERP helps companies improve their processes and increase their performance, but why do these types of implementations sometimes fail? Throughout this blog we will tell you why it happens, and we will share some tips to make the implementation of an ERP in your company successful.
In the process of implementing an ERP the two parties (client and implementer) seek the project to be a success; However, there are various factors that could affect the implementation of an ERP, according to the statistics shown by the erpfocus blog, 60% of ERP projects fail, and it is associated with poor management discipline when implementing an ERP.
Here are 3 large groups of factors that can affect implementation and how to avoid them.
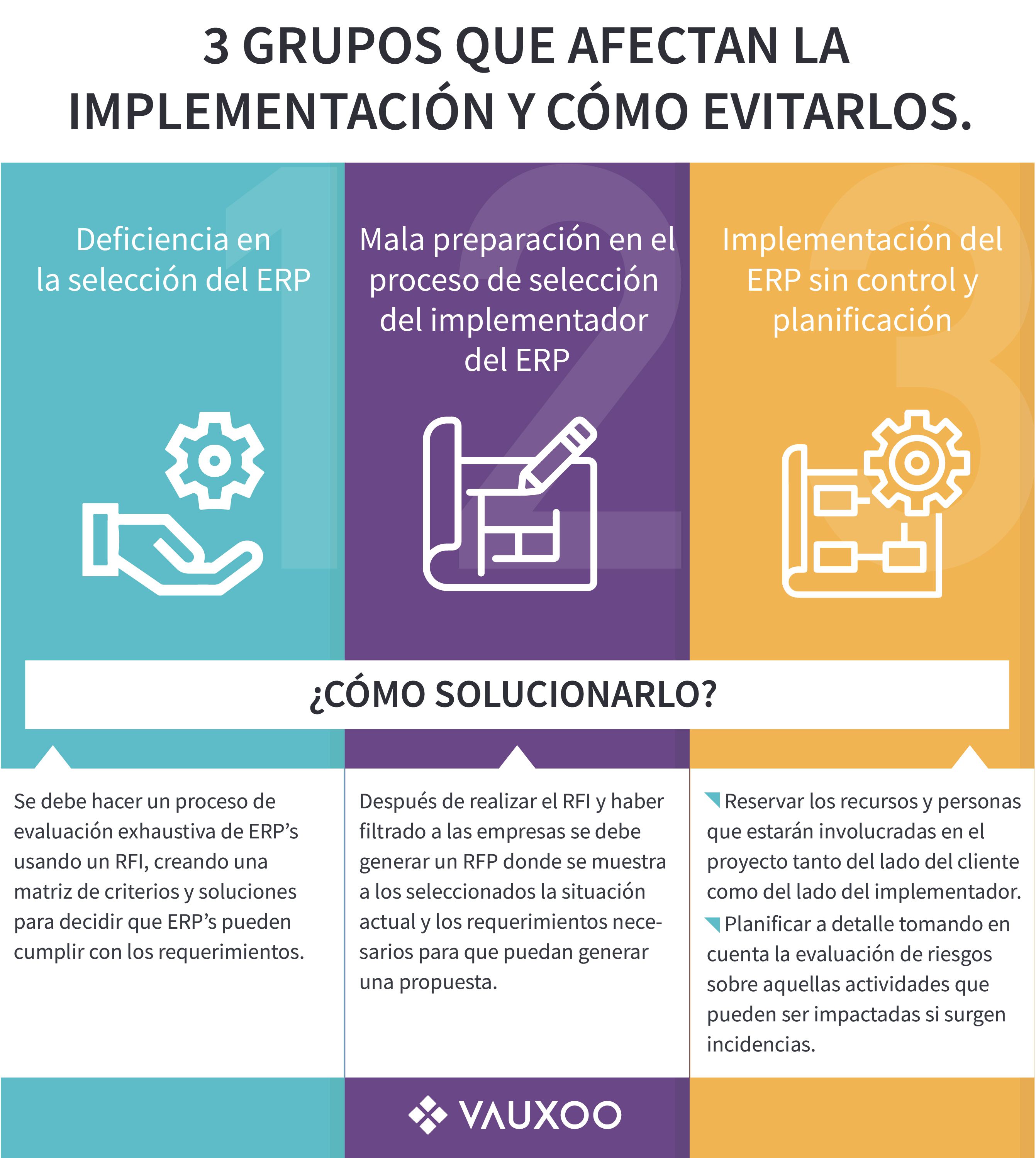
1. Deficiency in the selection of the ERP
Lack of tools for the future
In this new reality, companies need flexible, versatile and future-oriented solutions that allow them to cover the company's operation and also provide tools integrated into the ERP and that help both automate the operation and improve the customer experience, offering tools such as:
Communication apps (chat, surveys, electronic signatures, VoiP).
Marketing Apps (Email marketing, social marketing, SMS, Chat Bot).
Website apps (eCommerce and connectors with marketplaces, blogs, events, appointment management, websites, online learning).

When an ERP does not have these tools, companies will have problems in the future, since they will not be able to better face current challenges (Remote work schemes, business digitization, Marketing 5.0, among others). At this time, unfortunately companies will be forced to incur in developments or to contract integrations with other software to meet these needs, generating an overflow of project costs and times.
Do not foresee expansions to other countries
Acquiring a local solution (with tax and fiscal support only for one country) can be an alternative for many, however, today, the geographical limitations have almost come to an end and, on the contrary, the companies' strategy is being turning to enter new markets. Selecting an ERP that does not adapt to this reality, leads companies to quickly replace their current ERP in the face of expansion to the world, or what is more critical, to have different ERPs per country that are not linked to each other, making financial and operational consolidation impossible.
Selection of a software that does not allow decreasing.
Selecting a software that does not allow them to decrease in modules or licenses is a direct impact on the company's cash flow. Normally, companies aim to grow and increase their client portfolio, but sometimes due to different factors, clients can decrease and companies must continue to pay annuities for having acquired perpetual licensing models with maintenance annuities and clauses that do not allow them to decrease in number of user licenses.
Project scopes not measurable
This problem is generated when projects are based more on the expectation that the client has, than on a detailed analysis of the priorities, the phases, and the minimum viable deliverables. In these cases, we are faced with the project becoming very abstract and measuring the results obtained over time can become complex. It is estimated that 90% of clients that implemented an ERP fail to measure their return on investment. [1]
2. Poor preparation in the ERP implementer selection process
Search for the lowest cost implementer.
When doing the necessary searches to choose an ERP, companies usually filter by costs, one of the big mistakes is to select a provider where the consultancies seem very attractive in terms of costs and do not observe their quality.
Lack of information on the implementer's success stories.
It is crucial that the ERP implementer that your company selects is a strategic ally of the software publisher, that it has recognition, many success stories, implemented projects and that guarantees the success of the project.
Responsibility of the implementer in analyzing the scope of the project.
It is also important that the implementer take responsibility for helping your company define the scope of the project, what is the gap between what is needed versus what the tool does. It is essential that when choosing the implementer, you understand the tools they will use to analyze that return on investment.
3. ERP implementation without control and planning
Lack of control and planning on the client side
Little or no involvement of managers.
Many times company managers are not involved in the implementation, this part is critical because important strategic decisions are made within these projects.
People with little experience of the company within the project.
The people who know the company the most and are aware of all the processes within it must be placed to guarantee the success of the implementation project.
Lack of change management.
It is important that companies carry out change management processes for implementation that allow users to be motivated with the tool and with the change that is coming. 95% of companies that fail spend less than 10% of their budget on change management.[1]
Lack of control and planning on the implementer's side
Overcustomization of the ERP compared to the version that the editor offers by default.
Deficiency in the training strategy for key users and end users of the new system.
Poor master data preparation or lack of purification of discontinued or deprecated data from legacy systems.
Inadequate tests to the functionalities required by the user that do not allow closing the gap between what is required and what is offered by the software.
How to avoid these problems?

1. Those related to the deficiency in the selection of the ERP
To avoid the problem of lack of tools in the future, companies must do a formal process of evaluation of ERPs, which can be called Request For Information (RFI), in which the requirements that they expect the tool to include are raised to have a broader view of what an ERP vendor offers. Companies must make a thorough evaluation using a matrix of criteria and solutions.
An RFI should include criteria such as:
Functional requirements: This is the most important part, companies must explain what is the objective for which they seek to implement an ERP (Improve processes in production, keep a much more precise record in distribution, unite all areas of the company in a single system to keep a better control, among others). And based on this, ask questions focused on that objective to know how the ERP implementer can meet those requirements.
Evaluation of the implementer's success stories: A great factor to consider is whether the company that offers the ERP has carried out implementations with other companies in the same line of business. References of their work should be requested (success stories of the tool in other clients with a similar business).
This information is used as a filter to decide which ERP implementer can meet the requirements and have experience in implementing this type of business, to later learn more through demos, meetings, concept tests, among others.
Regarding the problem of scalability it is best to add these problems (Is the tool viable to use in other countries? Does it allow me to decrease in licenses or modules?, And Is there a segmentation by phases within the project?) To the matrix of evaluation criteria of the Request for Information (RFI).
2. Those related to the selection of the ERP implementer
After making a Request For Information (RFI) and having filtered the best companies that meet the criteria, a Request For Proposal (RFP) should be generated in which aspects of the current situation, and the necessary requirements are shown. A file with details such as:
The culture of the company.
The strategy and objectives of the project.
The current state and context of the company's situation.
Requirements and characteristics that are needed from the tool.
Requirements within the implementation project (Time and personnel for implementation).
The type of support that will be needed and in what areas.
The more the vendor and ERP implementer knows about the needs they have, the easier it will be for him to generate a proposal. The next step is to evaluate the proposals sent by the sellers, where the following must be evaluated:
The information on the implementer's trajectory.
Understanding the scope of the project, including a project timeline, and other details that help estimate costs.
List of requirements that the ERP already meets or can meet versus the current requirements of the company.
Delivery times.
References and qualifications of the implementer.
Quality in the gathering of requirements.
Budget and prices.
Contractual terms and conditions.
At the end, the best suppliers are selected, a request for a quote is generated and upon receiving a response from each one, we go to the phase of selecting the supplier that best suits the company's requirements to move on to hiring and signing agreements.
3. Those related to the implementation of an ERP
Ask the implementer to use a methodology that allows you to have a return of investment analysis (Return of Investment, ROI) or a gap analysis (GAP analysis), this will allow to measure the expectation, see what the tool really does and determine what savings will I have with the investment I am making against what I currently have.
Involvement of managers and people who can make decisions within the project.
Carry out an internal change management activity, parallel to the implementation of the project.
Reserve the resources and people who will be involved in the project both on the client side and on the implementer side.
Plan in detail taking into account the risk assessment of those activities that may be impacted if incidents arise.
Identify and maintain risk management throughout the project.
Remember that 60% of the ERP's that fail in the implementation are due to a lack of discipline and poor planning of the project, therefore, before starting to do an exploration of the ERP's that exist in the market, you must have a clear strategy and objectives planned by your company to be able to maintain that direction throughout the project, thus avoiding the possibility of these problems happening. In addition, the more you explore and analyze about those requirements that suppliers offer you, their trajectory and the involvement of your company is complete in the project, the greater the probability that you will reach the objectives set.